In this blog post, we will explore what an electrical circuit is and the key components that make up a basic electrical circuit. Understanding the fundamentals of electrical circuits is crucial for anyone working on electrical installation at dwelling and commercial units.
What is an Electrical Circuit?
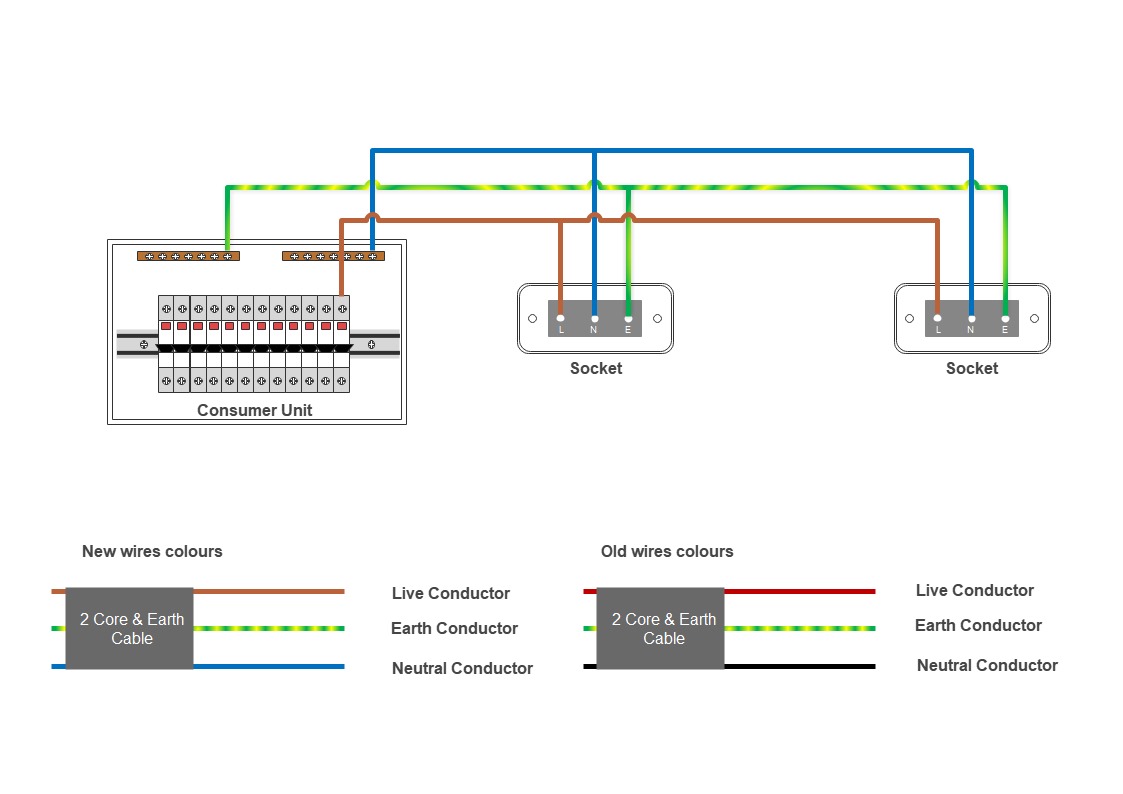
An electrical circuit is a closed loop path through which electric current can flow. It provides a means of transferring electrical energy from a source, such as a metered supply from a local substation, to a property, a battery or a generator. The current flows from the high potential (voltage) to the low potential, allowing work to be done.
| Component | Description |
| Source of electromotive force | Provides power to push electrons through the circuit |
| Conductive path | Wires that provide a path for electron flow |
| Load | Where electrical energy is consumed to do work (e.g. sockets, lights, electric showers, etc.) |
| Control elements | Regulate electron flow (e.g. switches, transistors) |
| Protection devices | Protect against overcurrent (e.g. fuses, circuit breakers) |
Need Electrical Help? Contact Slough Electrician Ltd now for expert, efficient solutions. Call us now to book an electrician for fast and reliable solutions!
The Key Components of an Electrical Circuit
There are several essential elements that make up a functioning electrical circuit:
Source of Electromotive Force
This is the source of power that pushes electrons through the circuit. It provides the voltage or potential difference needed for current to flow. Common sources are metered electric supply, batteries, solar panels, generators, etc. The greater the voltage, the stronger the push on the electrons.
Conductive Path
Copper electric Wires provide the path for electrons to flow. The circuit must form a complete closed loop for current to flow. An open circuit will stop the current flow.
Load
The load is where the electrical energy gets consumed, and work is done. It can be lights, heaters, electric showers or any other component that requires power to operate.
Control Elements
These components can control the flow of electrons. Examples include switches, transistors, relays, and integrated circuits. They allow turning the current on or off.
Protection Devices
These protect the circuit from excessive currents like shorts or overloads. Fuses, circuit breakers, and surge protectors are common protection devices.
How an Electrical Circuit Works
In operation, the source provides a voltage that gives electrons the energy to move through the conductive paths. The electrons flow through the circuit to the load where they work. After going through the load, they return to the source, completing the loop.
Control elements regulate the flow, while protection devices prevent damage from shorts or overloads. The result is a safe, controlled flow of electrical energy from source to load and back.
Understanding these basic components allows designing, building, and troubleshooting a wide range of useful electrical circuits. Whether it’s lighting, appliances, power supplies, motors, or computers, the same principles apply to provide efficient and safe electrical energy transfer.